What are we modeling? Using predictive fit to inform effect metric choice in meta-analysis
2025-10-09
Research Synthesis
The systematic integration of empirical results across multiple sources of evidence, for purposes of drawing generalizations1.
Meta-Analysis
Statistical models and methods to support quantitative research synthesis.
Fields that rely on research synthesis
- Medicine (Cochrane Collaboration)
- Education (What Works Clearinghouse)
- Psychology
- Social policy (justice, welfare, public health, etc.)
- Economics, international development
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Physical sciences
Some background on meta-analysis
The problem of effect metric choice
Proposal: Use predictive fit criteria to inform metric choice
Illustrations
Discussion
Canonical Meta-Analysis
We observe summary results from each of
- A summary random effects model:
- A random effects meta-regression:
- “Conceptual unity of statistical methods” for meta-analysis2 suggests that most any effect size measure
Prediction Interval
Effect Metric Menagerie
Effect Metric Families
Single-group summaries
- Raw proportions
- Arcsine-transformation
- Raw means
Bivariate associations / psychometric
- Pearson’s correlation
- Fisher’s
- Cronbach’s
Group comparison of binary outcomes
- Risk differences
- Risk ratios (log-transformed)
- Odds ratios (log-transformed)
- Bivariate models for
Group comparison of continuous outcomes
- Raw mean differences
- Standardized mean differences
- Response ratios (log-transformed)
- Probability of superiority
Metric choice methodology
Large literature on effect metrics for group comparison on binary outcomes.
Effect Metric Choice
Choice of metric is constrained by
Studies designs
Data availability, reporting conventions
Heterogeneity of study features (e.g., outcome scales)
Metric choice is driven by disciplinary conventions.
- In many applications, more than one metric could apply.
Metric choice by predictive fit criteria
Evaluate effect metrics by performance in predicting summary data for a new study.
- Data vector
- Data vector
- Use leave-one-out log-predictive density to measure predictive performance.
Two challenges
Polishing up models to generate predictions.
Conventional meta-analysis focuses on one-dimensional
Class attendance and college grades
Credé and colleagues19 reported a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies on association between class attendance and grades / GPA in college.
99 correlation estimates, samples ranging from
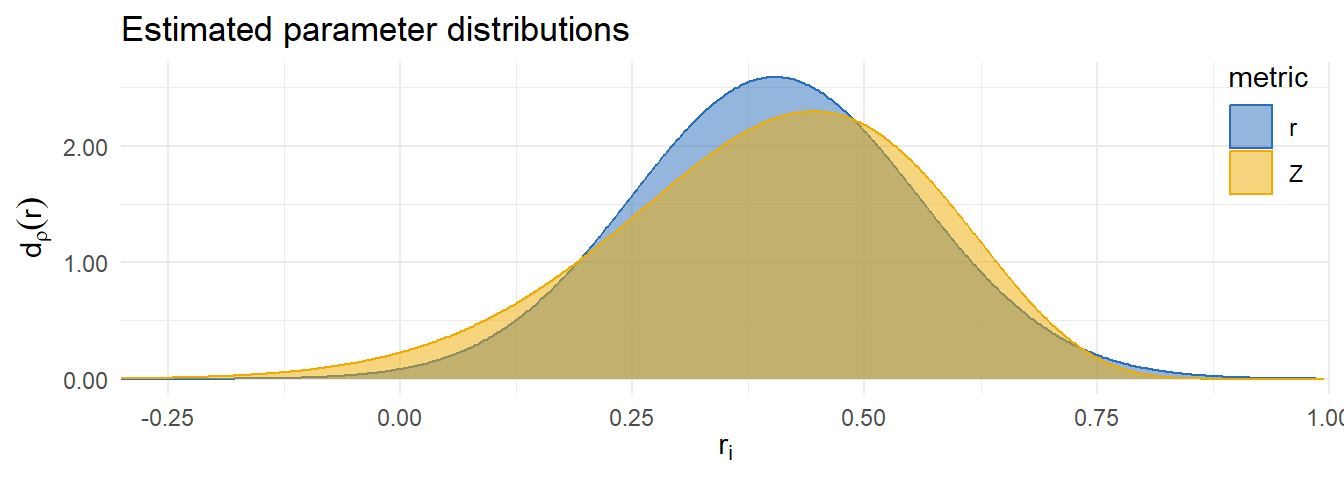
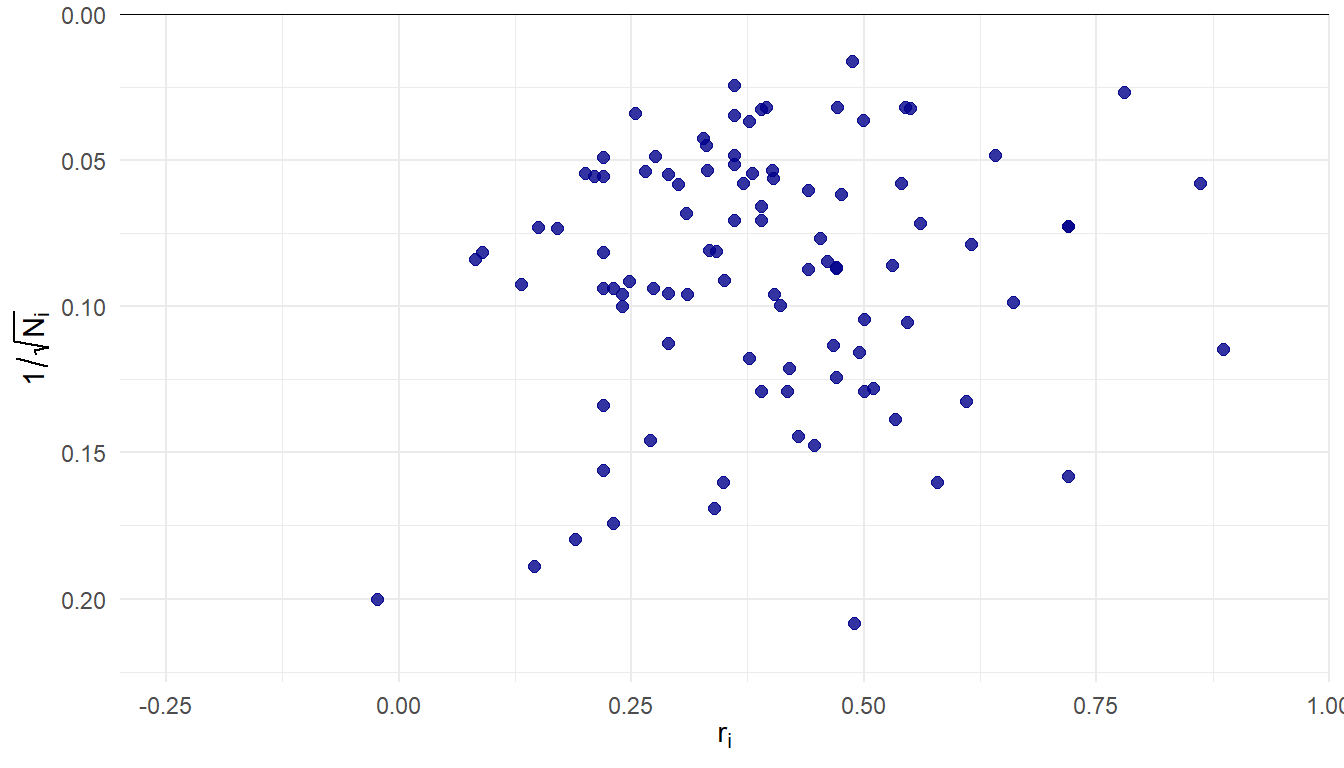
Bivariate associations
- The data: Pearson correlation between two variables of interest from a sample of
Effect size estimate
Predictive model:
Effect size estimate
Predictive model:
log-predictive density:
Metric comparison
| Metric | Est. | 95% CI | 80% PI | LPD | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | 0.40 | 0.37-0.44 | 0.20-0.60 | 0.34 | 0.09 |
| z | 0.41 | 0.37-0.45 | 0.16-0.61 | 0.22 | 0.12 |
| Difference | 0.12 | 0.05 |
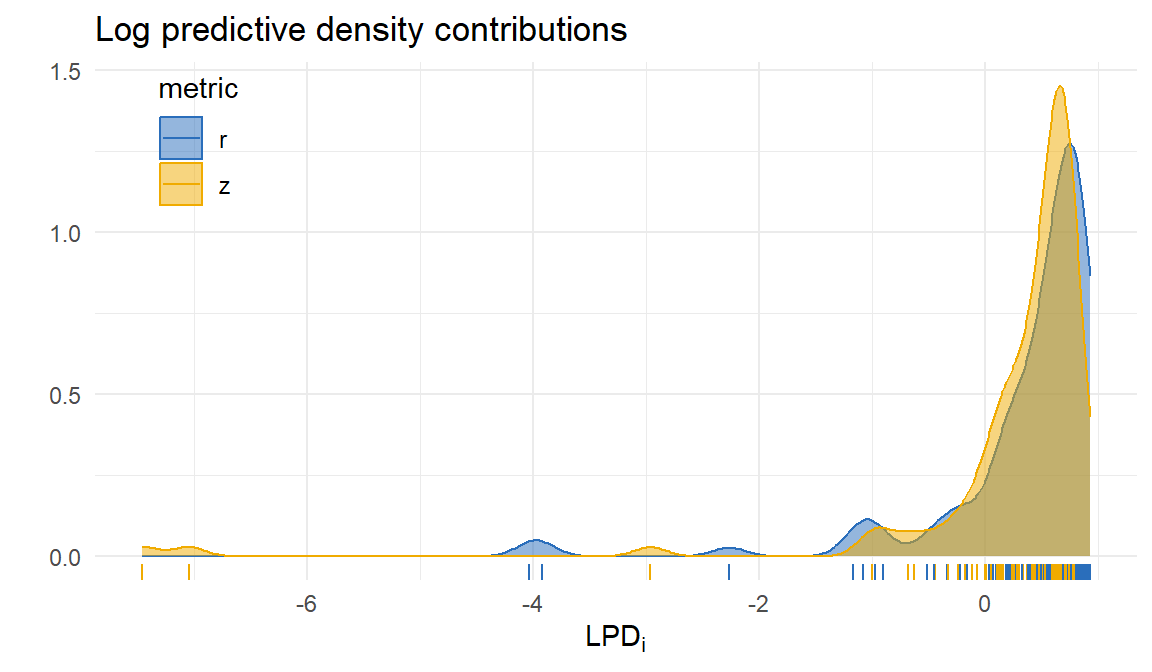
Outliers
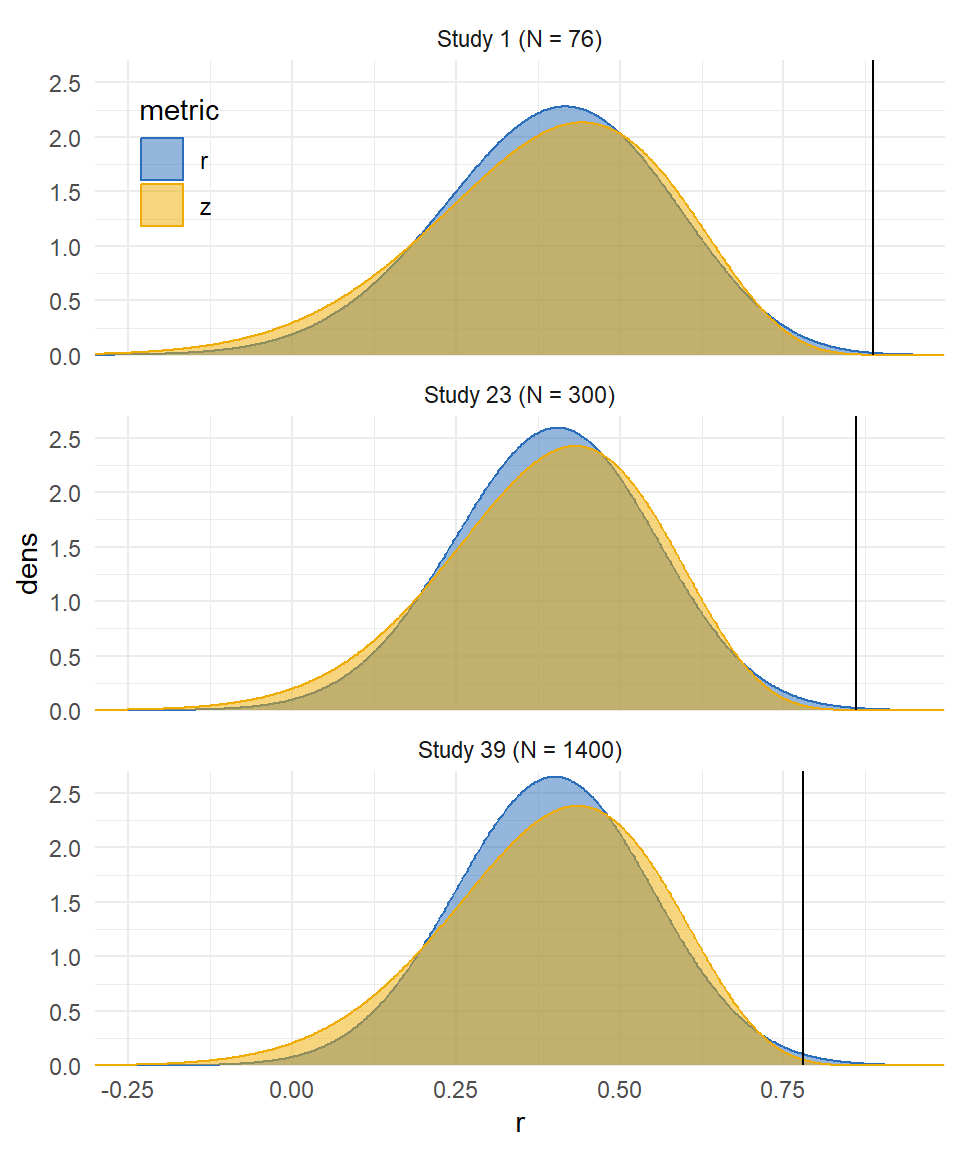
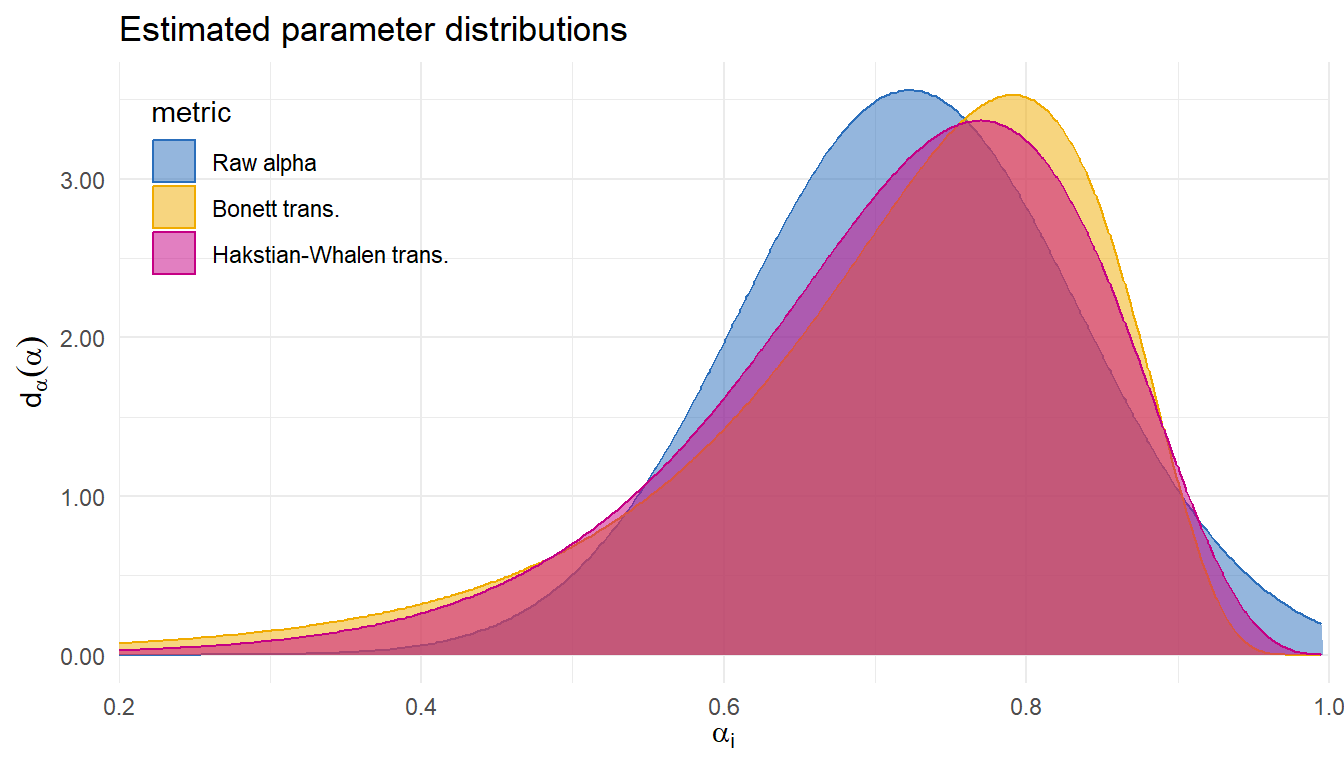
Reliability generalization of MIBS
Demir and colleagues20 gathered 33 estimates of internal consistency (Cronbach
Sample sizes ranging from
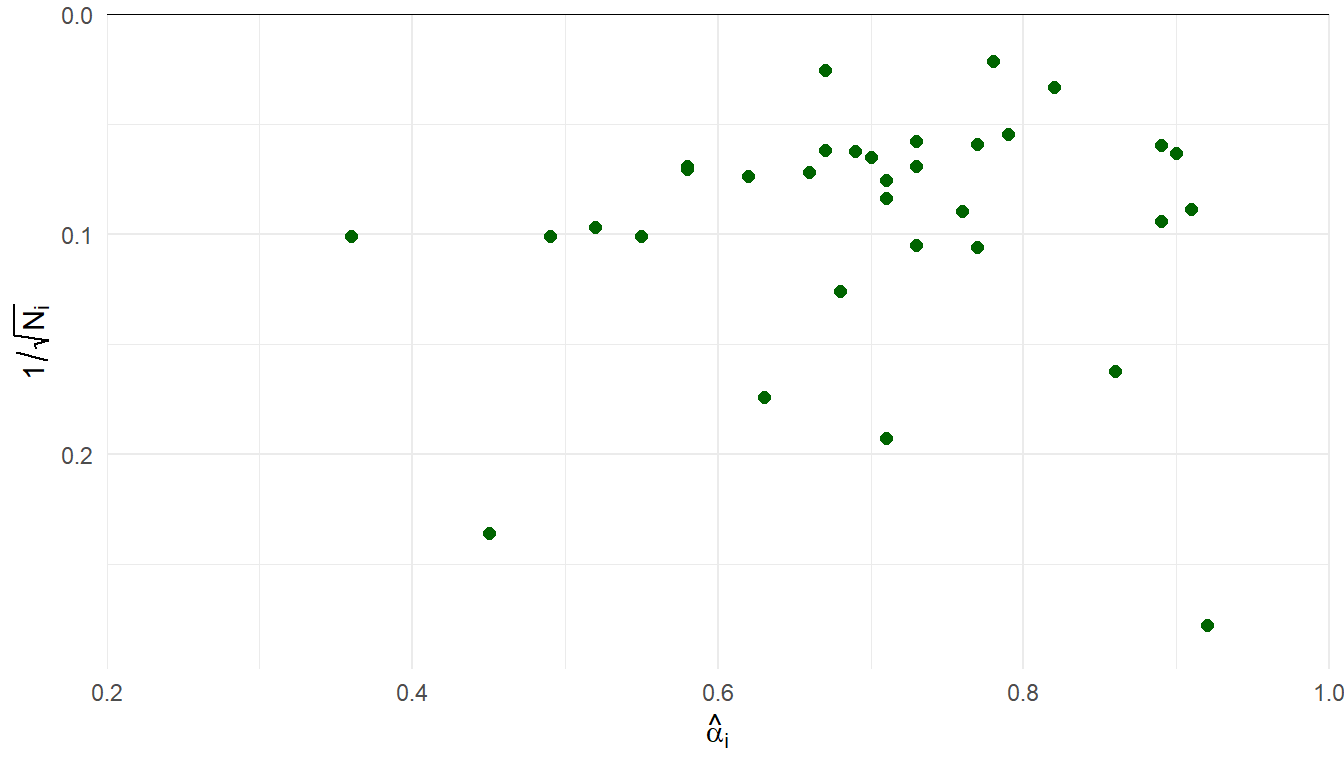
| Metric | Est. | 95% CI | 80% PI | LPD | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw alpha | 0.72 | 0.68-0.76 | 0.58-0.87 | 0.57 | 0.16 |
| Bonett trans. | 0.74 | 0.69-0.78 | 0.51-0.86 | 0.53 | 0.12 |
| Hakstian-Whalen trans. | 0.73 | 0.68-0.77 | 0.53-0.86 | 0.58 | 0.11 |
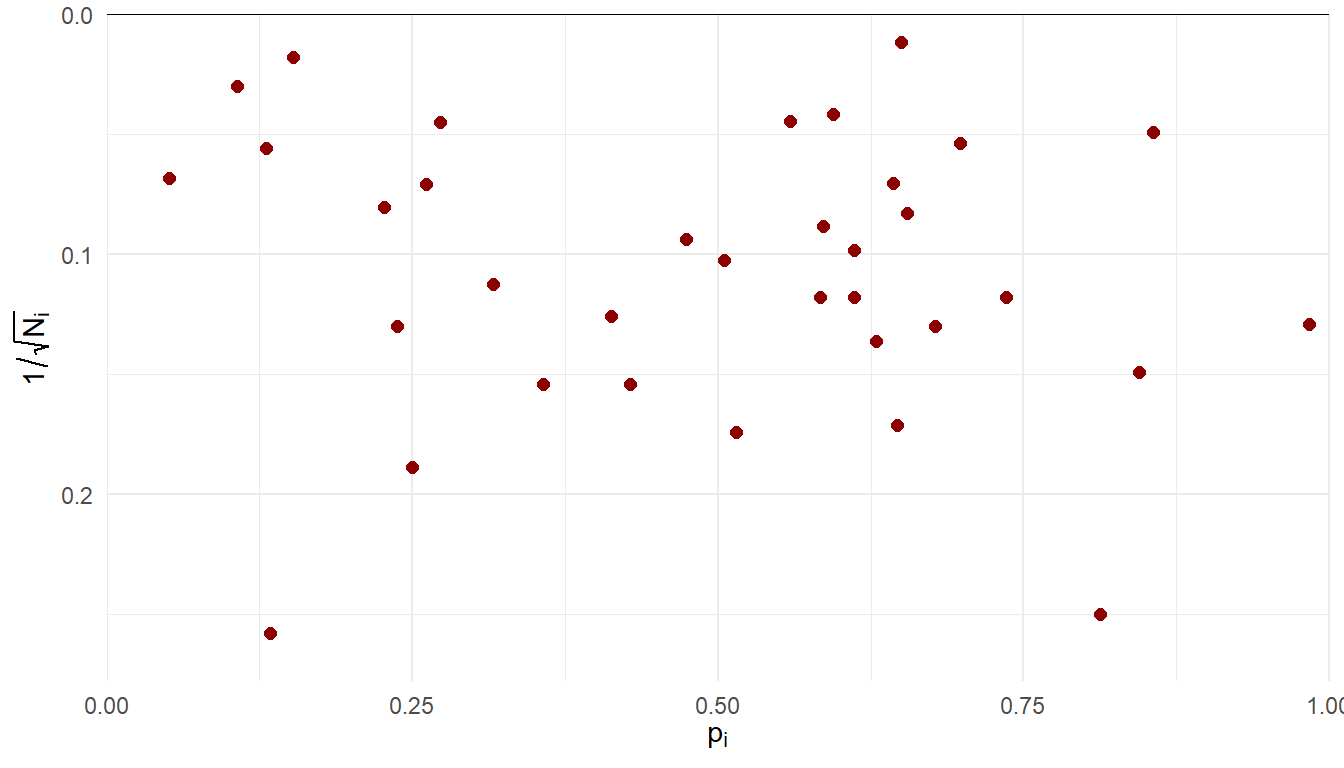
Incidence of olfactory loss in COVID-19 patients
Hannum and colleagues21 compiled data on rates of olfactory loss across 35 studies of COVID-19 patients.
Sample sizes ranging from
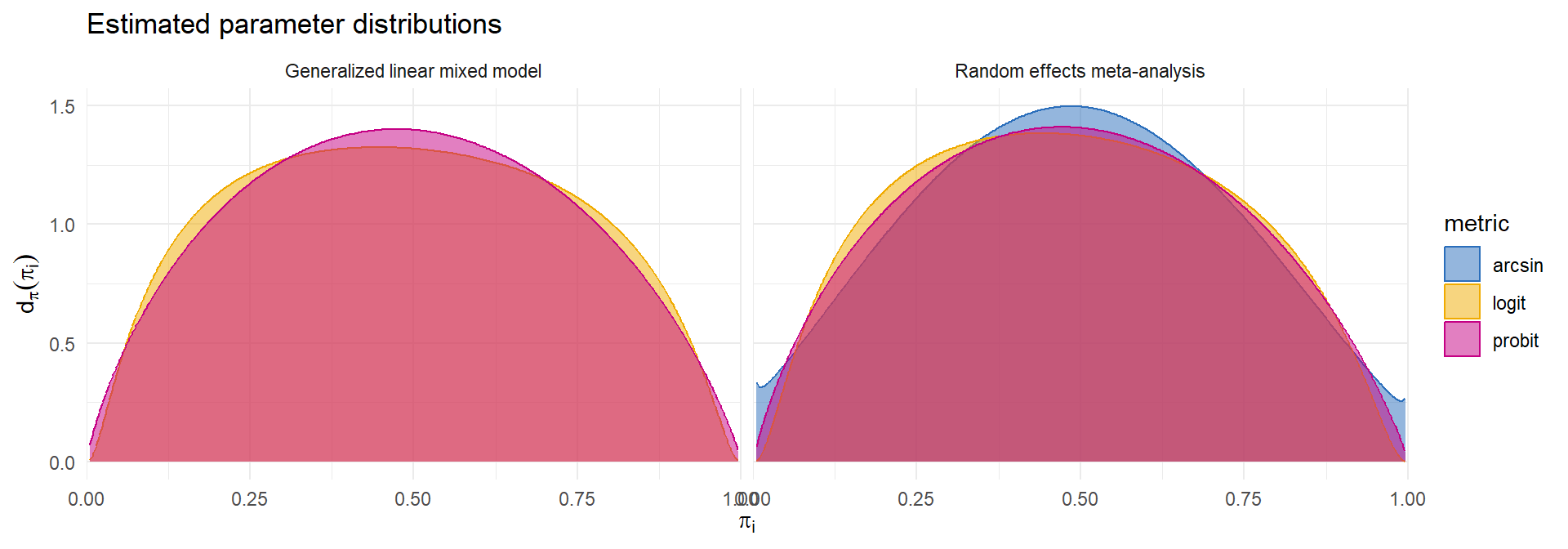
Many different transformations of
Could use conventional random effects model or generalized linear mixed model.
- Which predictive model to use?
Incidence of olfactory loss in COVID-19 patients
| Normal | Binomial | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Metric | Est. | 95% CI | 80% PI | LPD | SE | LPD | SE |
| RE | logit | 0.48 | 0.38-0.58 | 0.17-0.81 | -5.10 | 0.36 | -5.11 | 0.36 |
| RE | probit | 0.49 | 0.39-0.58 | 0.17-0.81 | -5.18 | 0.40 | -5.18 | 0.40 |
| RE | arcsin | 0.49 | 0.40-0.58 | 0.17-0.81 | -4.96 | 0.32 | -4.96 | 0.32 |
| GLMM | logit | 0.48 | 0.38-0.59 | 0.16-0.82 | -5.43 | 0.55 | ||
| GLMM | probit | 0.49 | 0.39-0.58 | 0.17-0.82 | -5.24 | 0.43 | ||
Effectiveness of nicotine replacement therapy
Cochrane Systematic Review of effects of nicotine replacement therapy vs. control on smoking cessation, defined as abstinence at 6+ month follow-up22.
Sample sizes ranging from
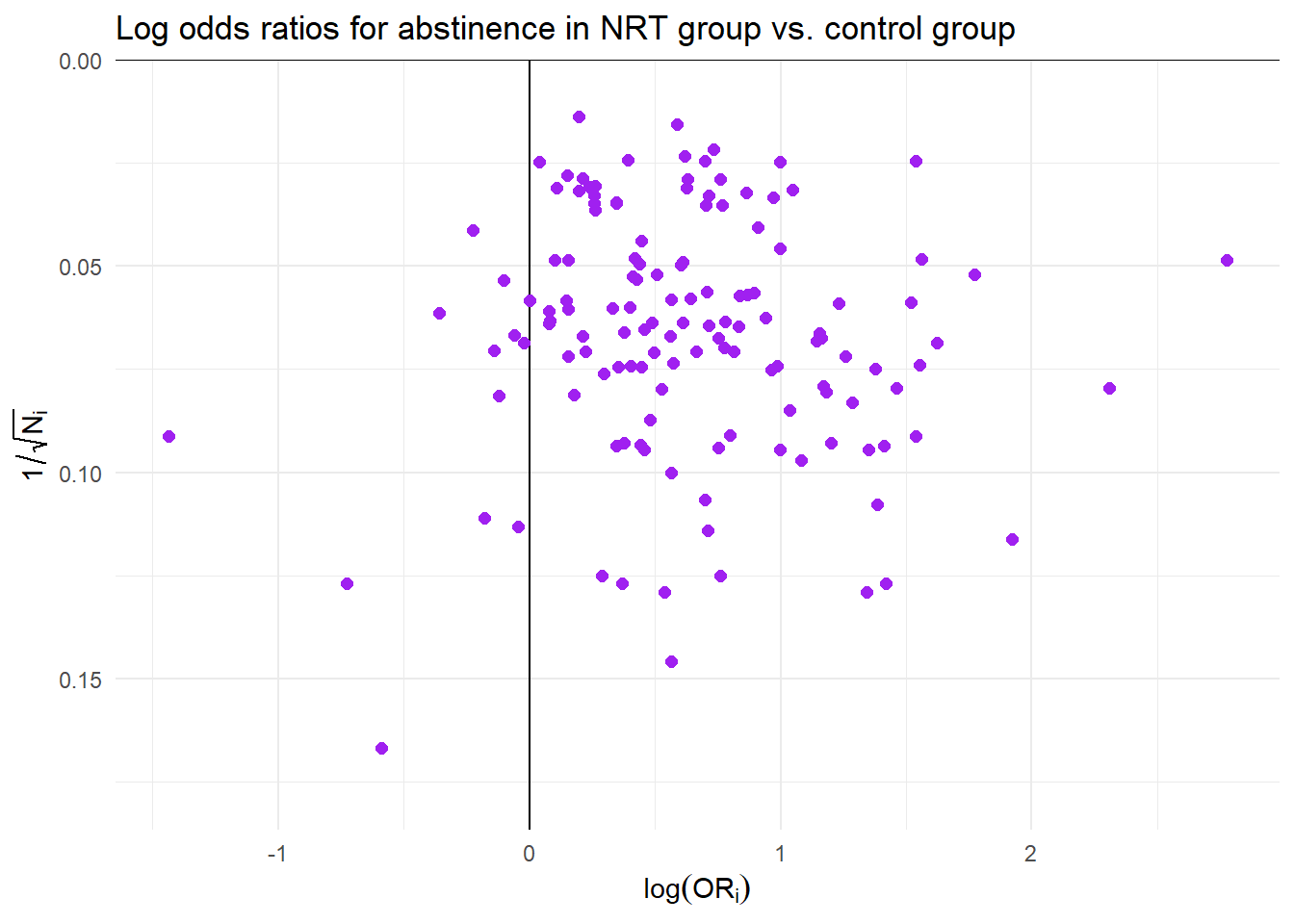
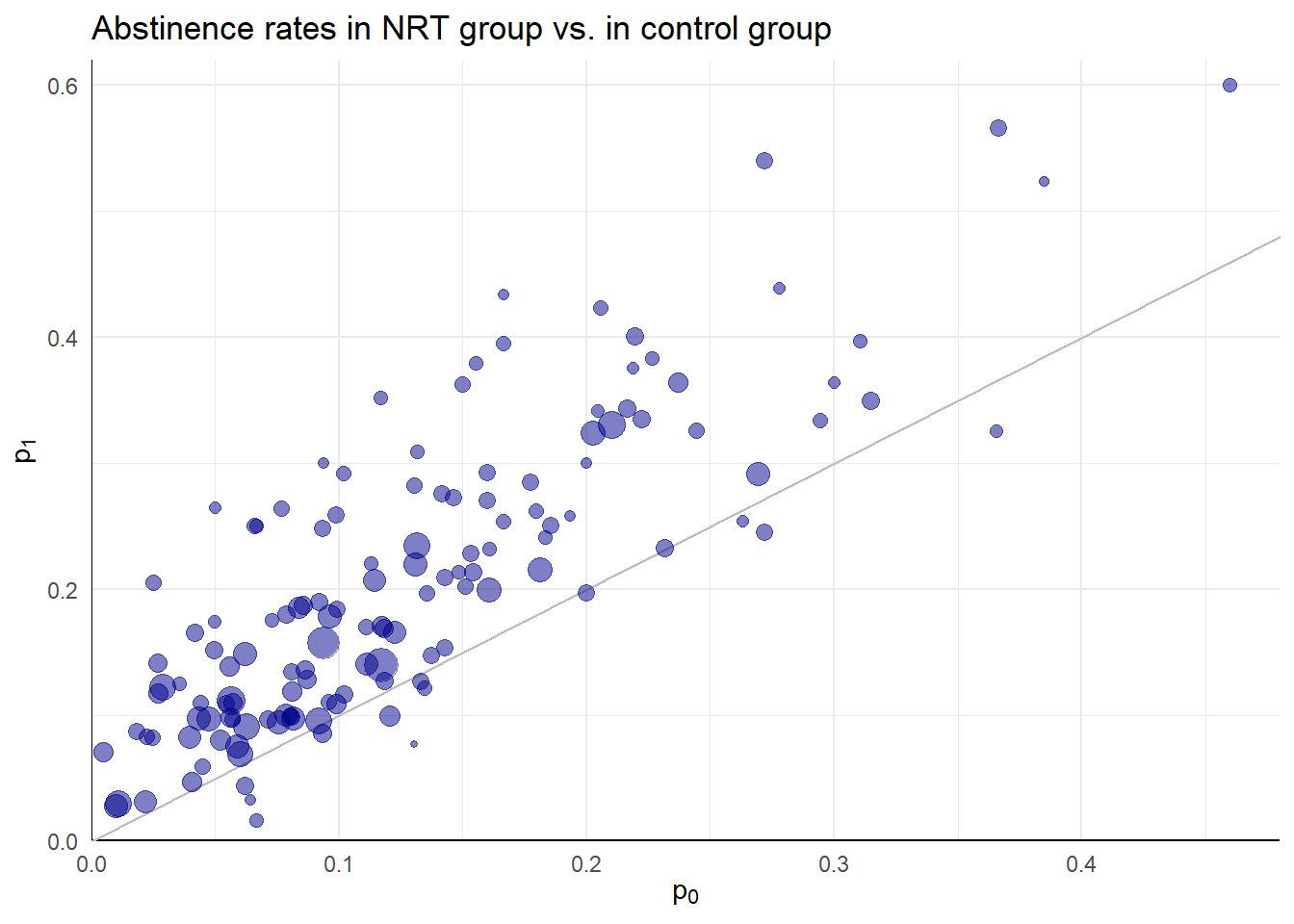
Random effects meta-analysis
- Difference ES metrics suggest very different implications and different heterogeneity
| Metric | Est | 95% CI | 80% PI | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk difference | 0.06 | 0.05-0.07 | 0.02-0.11 | 63.50 |
| Complementary risk ratio | 1.07 | 1.06-1.08 | 1.02-1.13 | 65.51 |
| Risk ratio | 1.57 | 1.48-1.66 | 1.23-1.99 | 36.88 |
| Odds ratio | 1.75 | 1.63-1.88 | 1.29-2.38 | 39.06 |
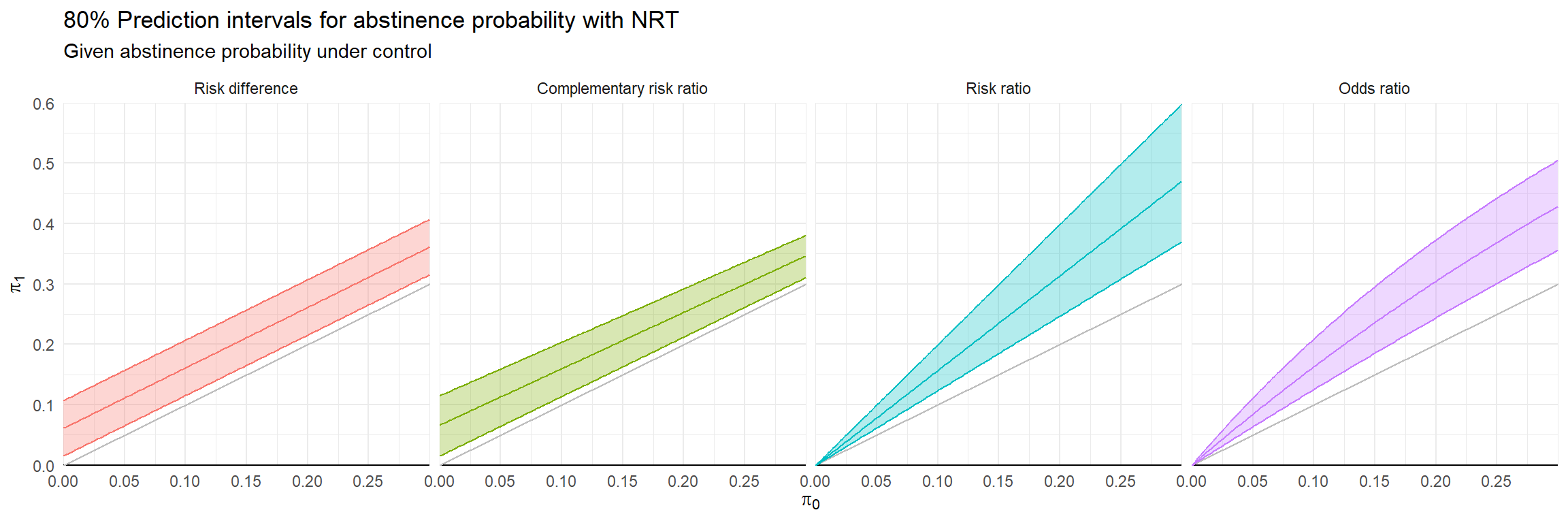
Effect metric comparison
Goal: evaluate predictions of
Conventional RE meta-analysis is a model for
Possible auxiliary models for
Random effects meta-analysis/meta-regression
Generalized linear mixed model
Beta-binomial regression
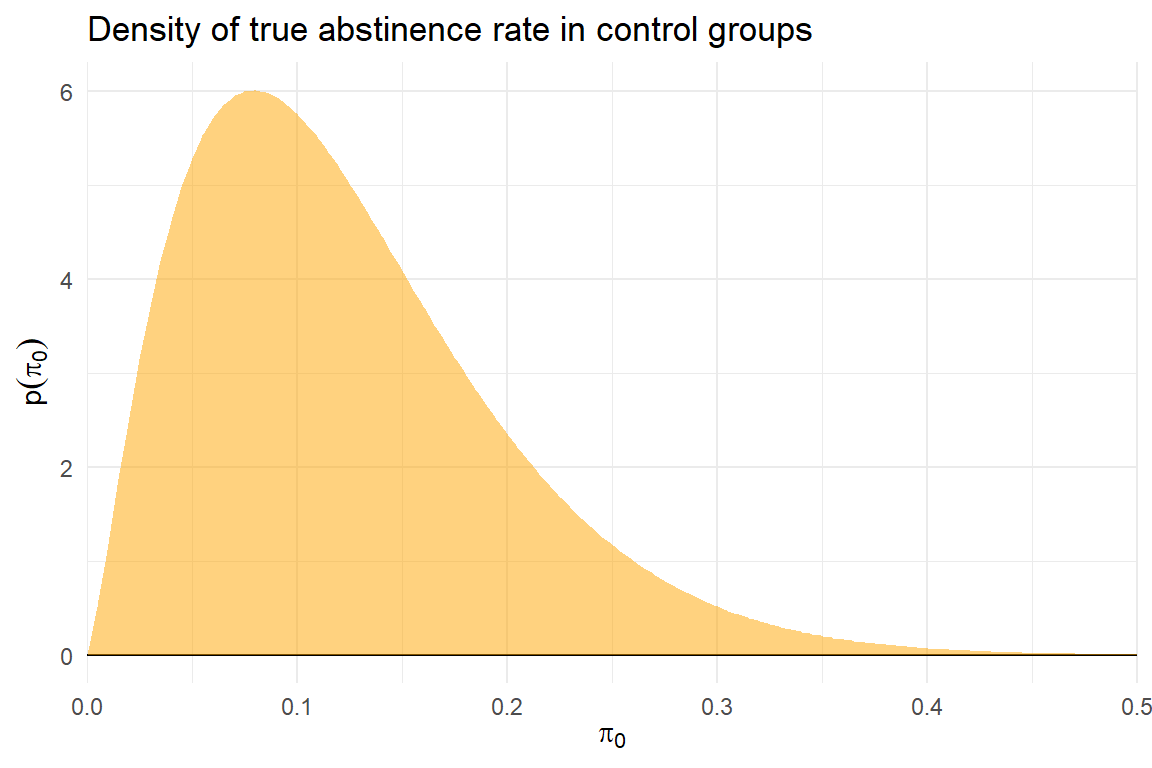
Predictive model
Metric comparison
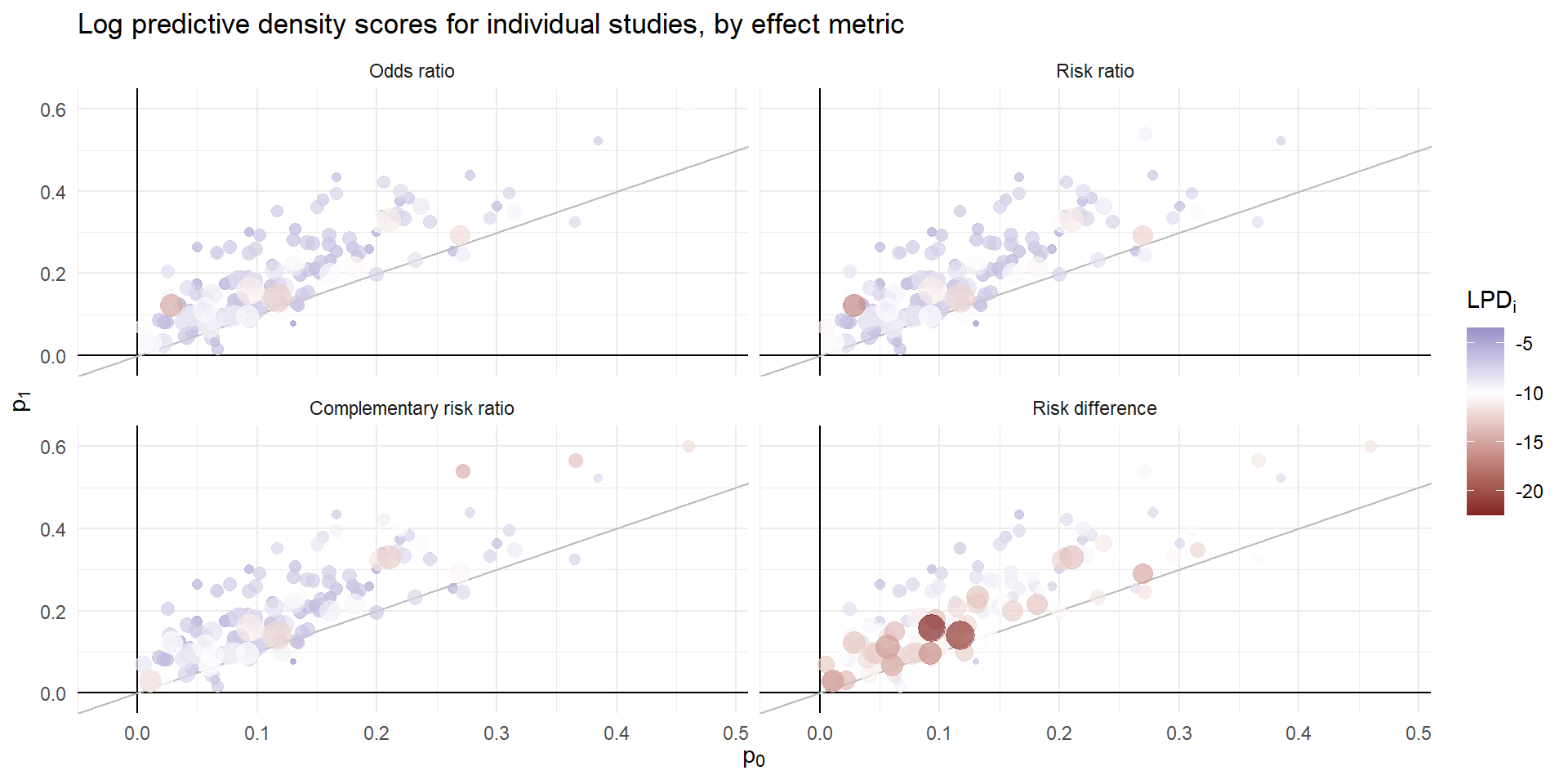
| Metric | LPD | SE | Diff. vs. OR | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds ratio | -7.300 | 0.151 | ||
| Risk ratio | -7.342 | 0.157 | -0.041 | 0.019 |
| Complementary risk ratio | -7.443 | 0.163 | -0.143 | 0.076 |
| Risk difference | -10.152 | 0.217 | -2.852 | 0.135 |
Predictive discrepancies
Discussion
Effect metric choice is a modeling assumption.
Predictive fit assessment is relevant and useful for meta-analysis.
Log predictive density calculations should be part of meta-analysts’ toolkit.
Will often require use of auxiliary models.
Advantages of log predictive density scoring
Allows comparison across effect metrics and different forms of models.
Auxiliary model building exercise can clarify scientific context.
Disadvantages and open questions
Deshpande and colleagues28 highlight discrepancies between LPD and other model evaluation metrics.
Other predictive scoring rules that may be relevant?
Is the joint distribution of
References
